The human brain is a remarkable and complex organ which acts as the control centre for the body.
As scientists continue to make new discoveries about what the brain does and how it works, educators can harness this growing body of knowledge to inform effective teaching and learning.
Ten Fascinating Facts About the Human Brain
Fact #1: Brains come in all different shapes and sizes!
Different animals have a range of brain structures. These can look quite different from the human brain, such as the rabbit and alligator brains below.
In fact, the brain of an octopus is distributed throughout the head and the arms of its body. Some animals, like sponges, don't have a central control system at all.
Fact #2: The brain consumes 20% of our energy requirements!
The human brain accounts for about 2% of our body weight but consumes 20% of our energy requirements.
The human brain is a very hungry organ!
Fact #3: The brain grows lots!
The brain doubles in size in the first year and reaches its largest size between 11 and 14 years of age.
Fact #4: The brain has over 100 trillion connections!
There are more connections between the neurons in the brain than stars in the Milky Way (over 100 trillion!).
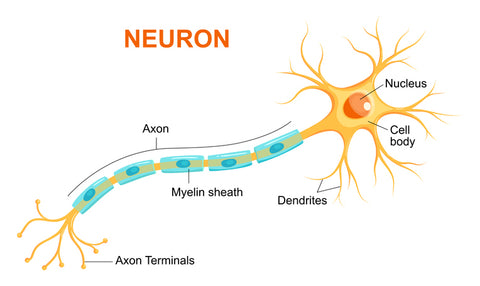
The brain contains 86 billion neurons. These cells are the basic building blocks of the brain. They transmit information throughout the brain and body as electrical and chemical signals.
Fact #5: The structure of our brain changes as we learn something new.
Repeated communication between neurons forms new connections that represent thoughts, memories or movements.
The brain's capacity to change and adapt like this over time is known as neuroplasticity.
Fact #6: The human brain does a lot of thinking.
The human brain can produce up to 50,000 thoughts a day.
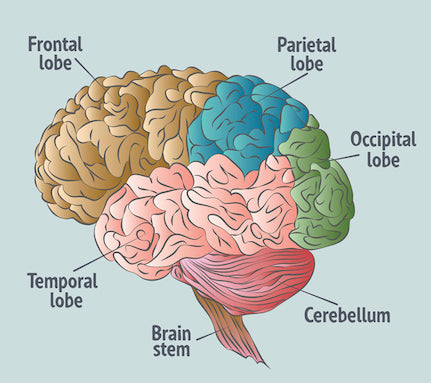
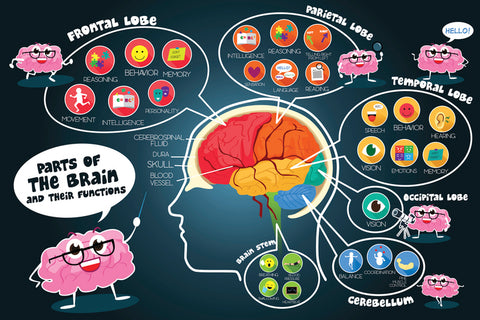
Fact #7: The human brain has four lobes.
The human brain has four lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe.
Each lobe is responsible for different functions such as thinking, sensation, movement, perception and memory.
Fact #8: Human brains react differently to smell.
Information relating to smell is treated differently by our brain to other sensory signals.
Most sensory information, including what we see, hear, touch and taste, is filtered through the thalamus before being sent on to the appropriate region of the brain.
However, smell travels directly to our limbic system, which generates instinctive and emotional responses based on memories and experiences.
That's why smells evoke powerful memories and the quickest way to calm the brain is with a comforting smell.
Fact #9: The brain's frontal cortex develops last.
The last area of the brain to develop is the frontal cortex. This area is responsible for impulse control and managing risk-taking behaviours.
Fact #10: The brain can’t feel pain.
Although the brain registers pain felt around the body, it has no pain receptors and is not capable of experiencing pain directly.
This allows the brain to process and respond to information without interruption.
If you would like to read more related topics on our blog, view our blogs on strengthening memory using visualisation, active learning and metacognition.







