#TheCompleteSeries6lessons
Your learners will focus on designing, developing, testing and prototyping computer-controlled electronic systems for rooms such as motion-sensor activated alarms, door buzzer entry systems or even ‘smart home’ automatic lights! While the lessons in this Complete Series are designed for you to use with your school’s Raspberry Pis and the free Scratch 2 programming software, all of the activities can be adapted to work with whatever physical computing resources you have. As well as working with electronic components and computer programming software, your children will learn all about influential computer scientists through history who have shaped the world around us. Not only that, but there are opportunities to make prototype models using DT materials OR 3-D CAD software to help develop ideas or to give inspirational product demonstrations!
Every lesson comes with highly detailed teacher’s notes which explain how to prepare and use electronic components and the child-friendly Scratch programming software. The notes also include additional background information about how various electronic components work and a range of printable help cards and safety information which you can share with your children.
Please note that these lessons are designed primarily for use with Raspberry Pi computers or PiTops, and the free programming software, Scratch. Some prior experience teaching computing is helpful, too!
#Lesson1EmbeddedSystems
Take a look at some everyday products containing electronic components and consider how they might work. The included slides with this lesson explain how many electronic products are monitored and controlled by computer systems embedded in them, and that these systems store computer programs written especially for them.
After that, challenge children to start writing, in human language, algorithms which explain how everyday electronic products might work.
This downloadable lesson includes a lesson plan, slideshow presentation and printable teaching resources.
What's included:
- Lesson plan
- Slides
- Activity ideas
- Teacher’s notes
- A Brief History of Computer Science info. sheet
- Differentiated worksheets
#Lesson2ControllingCrossings
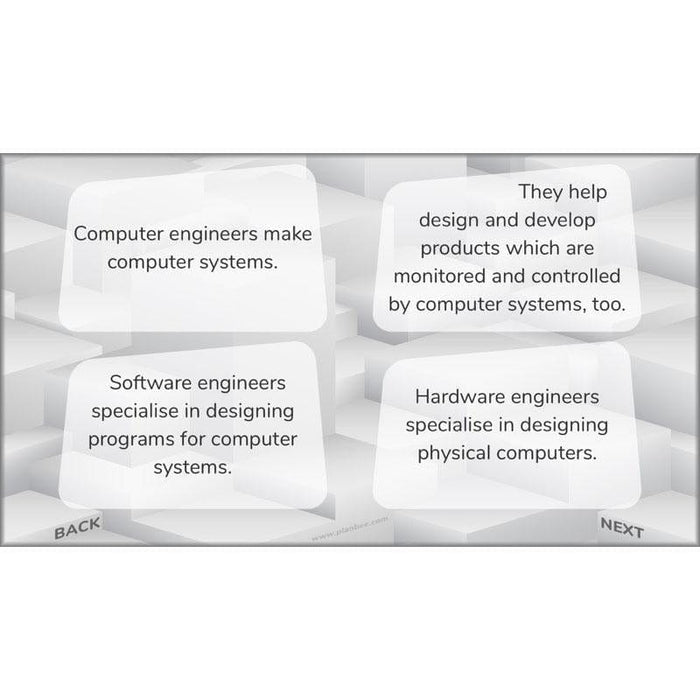
Find out what it is that computer hardware and software engineers do, then consider a problem they might encounter when helping design products: how are pedestrian crossings programmed and controlled by computer systems?
Children may then either design and program pelican crossings purely ‘in software’ using the provided Scratch project files, or using a combination of Scratch software and actual electronic components.
This downloadable lesson includes a lesson plan, slideshow presentation and printable teaching resources.
What's included:
- Lesson plan
- Slides
- Activity ideas
- Teacher’s notes
- Differentiated worksheets
- Challenge card
- Scratch software project files
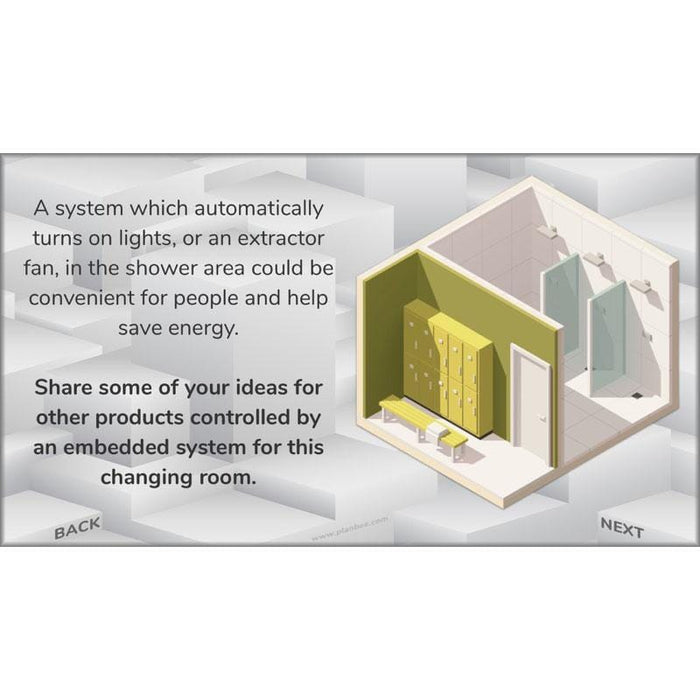
#Lesson3RoomSystems
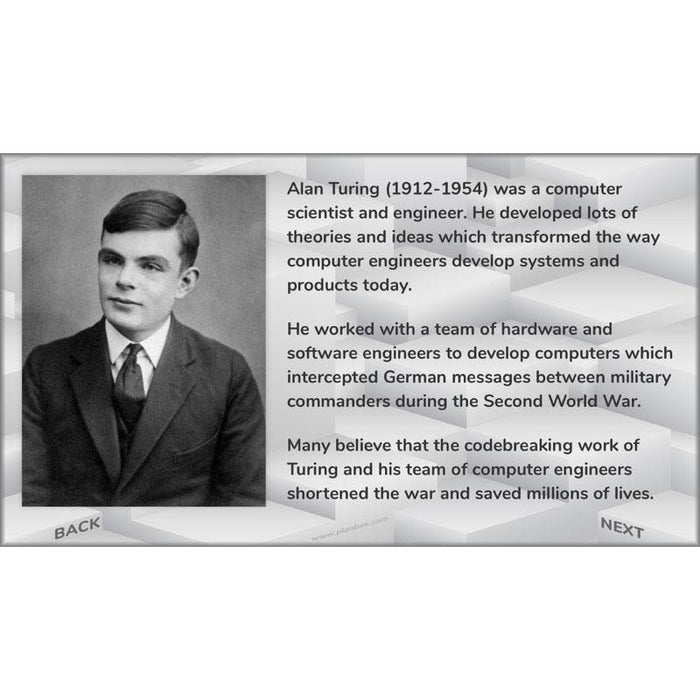
Take a closer look at embedded computer systems which monitor and control the products around us. The included slides also explain how pioneering computer scientists began to make computers and programming languages that were easier for people to use during the 1940s, 1950s and 1960s.
After that, challenge children to begin designing their own products such as automatic lights or alarms that could be installed in rooms.
This downloadable lesson includes a lesson plan, slideshow presentation and printable teaching resources.
What's included:
- Lesson plan
- Slides
- Activity ideas
- Teacher’s notes
- Differentiated worksheets
- Design an Embedded Room System help sheet
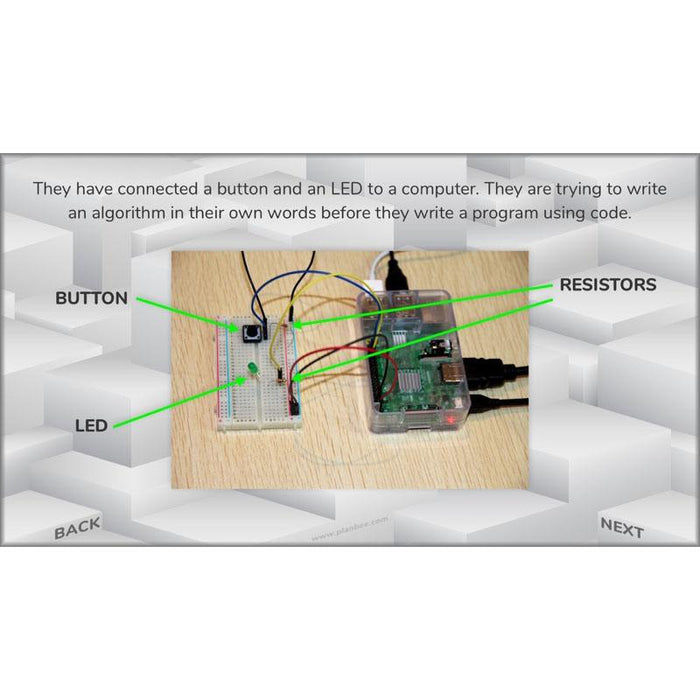
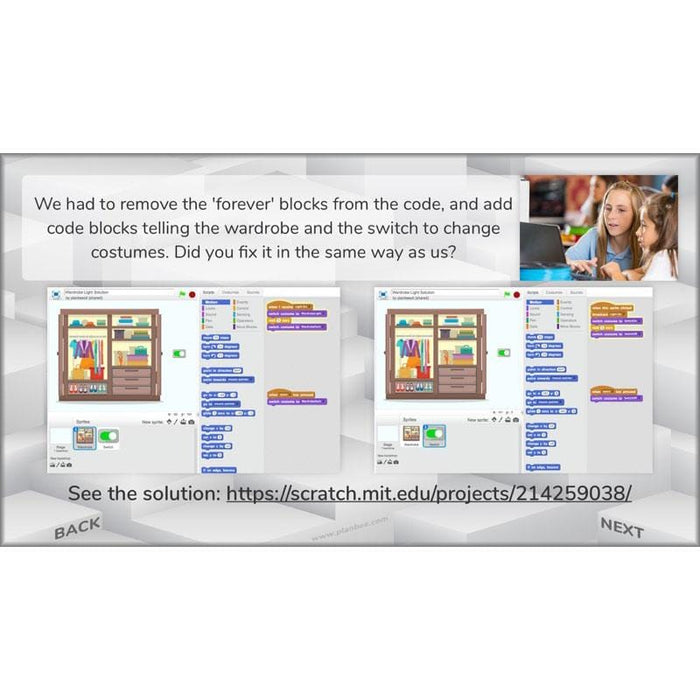
#Lesson4ProgrammingProducts
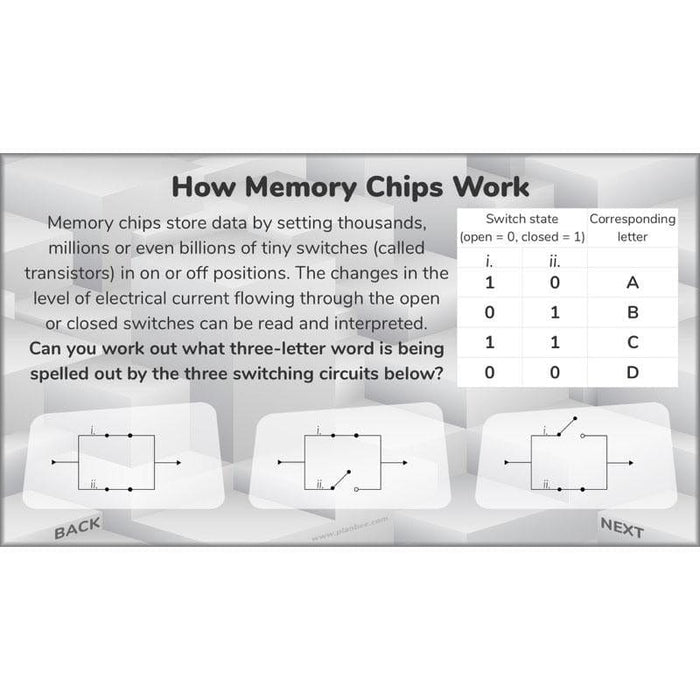
In this lesson, children will learn more about how and why inexpensive microcontrollers are used to control electronics in everyday products.
After that, they’ll either go on to wire up simple electronic components for a room system, such as a doorbell or automatic light (and program them to work), or consider how a novelty electronic toy might be programmed to work.
This downloadable lesson includes a lesson plan, slideshow presentation and printable teaching resources.
What's included:
- Lesson plan
- Slides
- Activity ideas
- Differentiated worksheets
- ‘Connecting Components’ cards
- Teacher’s notes
#Lesson5PrototypeModels
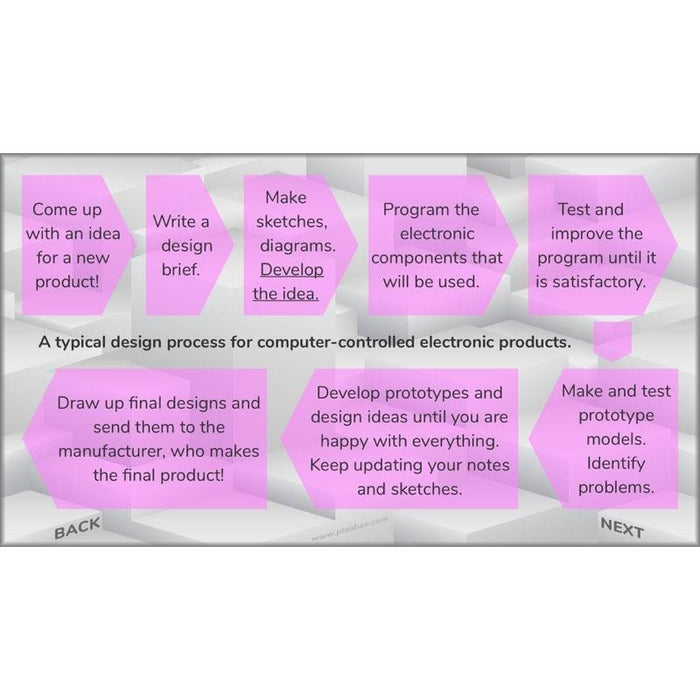
Why do we make prototype models? The included slides challenge children to consider this, then go on to explain why models are helpful both for developing and explaining ideas.
After that, there’s a choice of activities where children may either make shoebox model rooms to help develop and explain their electronic room systems that they’ve designed previously, or use CAD software to design 3-D models.
This downloadable lesson includes a lesson plan, slideshow presentation and printable teaching resources.
What's included:
- Lesson plan
- Slides
- Activity ideas
- Differentiated worksheets
- Teacher’s notes
#Lesson6Whathavewelearned
Having learned all about how electronic products are programmed and controlled, then gone on to design and develop their own computer-controlled product ideas, it’s time to reflect and evaluate!
The included slides with this lesson pose a number of questions about children’s prior learning, and during either of the two learning activities included, children will evaluate their own learning and design processes as well as consider how they helped, and were helped, by others in their class.
This downloadable lesson includes a lesson plan, slideshow presentation and printable teaching resources.
What's included:
- Lesson plan
- Slides
- Activity ideas
- Differentiated worksheets
- Teacher’s notes
Free Overview (Medium-Term Plan)
Download a free overview to support your teaching of this scheme of work.
Free Assessment Grid
Download a free, editable assessment grid to support your teaching of this scheme of work.
Curriculum Objectives covered
- KS2 - use research and develop design criteria to inform the design of innovative, functional, appealing products that are fit for purpose, aimed at particular individuals or groups
- KS2 - generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas through discussion, annotated sketches, cross-sectional and exploded diagrams, prototypes, pattern pieces and computer-aided design
- KS2 - select from and use a wider range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks [for example, cutting, shaping, joining and finishing], accurately
- KS2 - evaluate their ideas and products against their own design criteria and consider the views of others to improve their work
- KS2 - understand how key events and individuals in design and technology have helped shape the world
- KS2 - understand and use electrical systems in their products [for example, series circuits incorporating switches, bulbs, buzzers and motors]
- KS2 - apply their understanding of computing to program, monitor and control their products